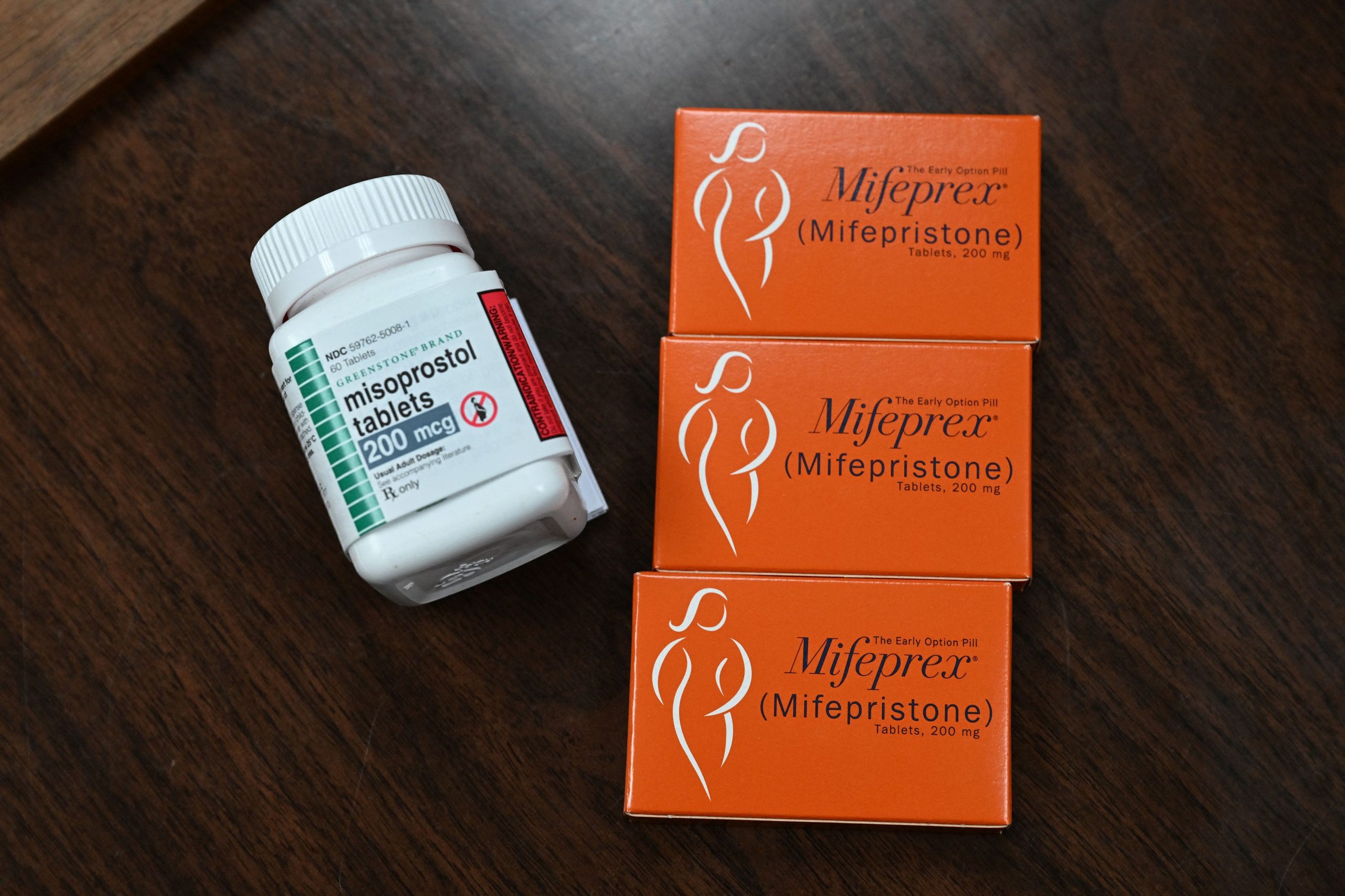
No, misoprostol isn’t available over-the-counter in most countries. This restriction exists due to safety concerns requiring medical supervision. However, access varies significantly depending on location. Research your country’s specific regulations before considering any action.
Several organizations offer information on accessing abortion services, including safe options for medication abortion using misoprostol. These resources often provide guidance on finding healthcare providers or telehealth services capable of providing the necessary support and medical advice. Remember, reliable sources are critical for your safety.
Always consult a healthcare professional before using misoprostol. Self-treating can lead to complications. A doctor can assess your individual health needs and provide the appropriate guidance and support. This ensures the safest and most effective outcome.
Finding a reputable source for accurate information is paramount. We strongly recommend utilizing official healthcare websites and trusted organizations focused on reproductive health. Misinformation can be dangerous; protect your health by seeking verified data.
- Misoprostol Over the Counter: A Comprehensive Guide
- What is Misoprostol and How Does it Work?
- Countries Where Misoprostol is Available Over the Counter
- Legality and Regulations Regarding OTC Misoprostol
- Potential Risks and Side Effects of Misoprostol
- Serious Side Effects
- Precautions
- Monitoring Your Health
- Dosage and Administration of OTC Misoprostol
- Oral Administration
- Common Side Effects
- Storage
- Alternative Methods for Medication Abortion
- Understanding Your Options
- Seeking Medical Advice Before Using Misoprostol
- Understanding Your Health History
- Assessing Your Situation
- Managing Potential Risks
- Post-Treatment Follow-Up
- Finding Reliable Information
- Alternative Treatment Options
- Finding Reliable Information on Misoprostol
- Checking Source Credibility
- Accessing Reliable Information
- Avoiding Misinformation
- Understanding Limitations
- Emergency Contraception vs. Misoprostol for Abortion
- Emergency Contraception
- Misoprostol for Abortion
- Key Differences
Misoprostol Over the Counter: A Comprehensive Guide
Misoprostol is not available over the counter in most countries. Its sale is restricted due to safety concerns and the need for medical supervision.
However, access varies considerably. Check your country’s regulations; specific laws differ significantly.
If you are considering using misoprostol for medication abortion, consult a healthcare professional. They can provide accurate information, guide you through the process safely, and address any potential complications. Self-treating carries risks.
For reliable information on medication abortion, explore resources like the World Health Organization (WHO) or trusted family planning organizations in your region.
| Country | Over-the-counter Availability | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| United States | No | Prescription required. |
| Canada | No | Prescription required. |
| United Kingdom | No | Prescription required. |
| Mexico | Potentially, with restrictions | Regulations vary regionally. Verify legality and safety before purchasing. |
Remember: The information above is for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for guidance on your specific circumstances.
What is Misoprostol and How Does it Work?
Misoprostol is a medication primarily used to prevent stomach ulcers and induce labor. It’s a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analogue.
To prevent ulcers, it reduces stomach acid production. In inducing labor, it softens and thins the cervix, preparing it for dilation and eventual delivery. This action mimics the natural process of the body. The exact mechanism involves stimulation of uterine contractions.
It’s crucial to understand that Misoprostol’s use for inducing abortion carries risks. Only a healthcare professional can assess these risks and provide guidance.
| Use | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
| Ulcer Prevention | Reduces stomach acid secretion |
| Labor Induction | Cervical softening and uterine contractions |
Always consult a doctor before using Misoprostol, especially if pregnant. They can discuss the potential benefits and risks specific to your situation. Misoprostol’s usage should be under medical supervision. Improper use can lead to severe complications.
Countries Where Misoprostol is Available Over the Counter
Availability of misoprostol without a prescription varies significantly. Always confirm local regulations before purchasing.
- Mexico: Misoprostol is readily available in many pharmacies without a prescription.
- Some countries in South America: Several South American nations allow over-the-counter sales, though specific regulations change by country. Always verify local laws. Countries like Brazil and Colombia have had varying degrees of accessibility.
- Parts of Africa: Access varies considerably across African countries. Some regions may allow over-the-counter purchase, while others require a prescription. Local regulations determine accessibility.
- Some countries in Asia: Similar to Africa, some Asian nations may permit over-the-counter sales, but this is not uniform across the continent. Individual country laws dictate availability.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for guidance on medication use. Regulations regarding over-the-counter medications frequently change.
- Check your local pharmacy regulations.
- Seek medical advice for any health concerns.
- Verify the source of any medication before use.
Legality and Regulations Regarding OTC Misoprostol
Misoprostol’s availability over the counter varies significantly across countries. In some nations, like many in Latin America and parts of Africa, it’s legally available without a prescription for various indications, including inducing labor. However, in other countries, including the US and many European nations, it requires a prescription. Check your country’s specific regulations. You should consult a healthcare professional before using misoprostol, regardless of its legal status in your area. This is critical for ensuring safe and appropriate usage.
Regulatory bodies often control the sale and distribution of misoprostol. These regulations aim to minimize misuse and ensure patient safety. These include restrictions on packaging, labeling requirements (e.g., clear instructions and warnings), and potential limitations on the quantity that can be purchased without a prescription. Always adhere to these guidelines. Ignoring them could result in legal repercussions.
The legality and availability of misoprostol are subject to change. Therefore, always verify the current legal status and regulations in your jurisdiction before acquiring or using the medication. Reliable sources of information include your national health authority’s website and trusted healthcare providers.
Remember, self-treating can be risky. Consult a doctor or other licensed medical professional for personalized advice on using misoprostol or any other medication. They can provide guidance based on your individual health needs and circumstances, ensuring you make informed decisions.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Misoprostol
Misoprostol, while effective, carries potential risks. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and fever. These usually resolve within 24 hours.
Serious Side Effects
More serious, though rare, complications can occur. These include heavy bleeding requiring medical intervention, infection, incomplete abortion (requiring further treatment), and allergic reactions. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience excessive bleeding (soaking more than two maxi pads per hour), severe abdominal pain, high fever (over 100.4°F or 38°C), or signs of infection (foul-smelling discharge, increased pain).
Precautions
Prior medical conditions matter. Inform your doctor about any existing health issues, such as heart conditions, kidney problems, or blood clotting disorders, before using misoprostol. It’s also crucial to disclose any medications you’re currently taking. Misoprostol isn’t suitable for everyone. Your doctor will determine if it’s the right option for you.
Monitoring Your Health
After taking misoprostol, monitor your body closely for any unusual symptoms. Keep track of bleeding levels and report any concerning changes to a medical professional. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Post-procedure follow-up is recommended to ensure complete abortion and address any complications.
Dosage and Administration of OTC Misoprostol
Follow the instructions on your specific misoprostol packaging carefully. Dosage varies depending on the product and the intended use. Typically, for medication abortion, you’ll take a specific number of tablets orally. The exact number and timing are crucial and should be precisely followed. Always read the included leaflet.
Oral Administration
Misoprostol tablets are typically taken orally with water. Avoid crushing or chewing the tablets, unless specifically instructed otherwise in your product’s instructions. Take the medicine at the recommended times. You may experience some side effects, which are usually mild and temporary.
Common Side Effects
Expect some cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or fever. These are usually manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-nausea medications. If you experience heavy bleeding, severe pain, or any other concerning symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Storage
Store misoprostol as directed on the product label. This usually involves keeping it in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Ensure children cannot access it.
Alternative Methods for Medication Abortion
If medication abortion isn’t accessible, surgical abortion is a safe and common alternative. This procedure involves a minor surgical intervention to remove the pregnancy. Consult a healthcare provider to determine if it’s the right option for you.
Understanding Your Options
Your healthcare provider can discuss the procedure, risks, recovery time, and answer any questions. They will also guide you through the process, including pre-procedure instructions and post-operative care. It’s crucial to have open communication with your doctor.
Another option to consider, depending on your circumstances and location, is traveling to a clinic or state where abortion is legal and accessible. Factors such as distance, cost, and time commitment should influence this decision.
Remember, accessing accurate and unbiased information is paramount. Reliable sources such as Planned Parenthood or your local health department can provide comprehensive resources about abortion options.
Seeking Medical Advice Before Using Misoprostol
Always consult a healthcare professional before using misoprostol, especially if you’re considering medication abortion.
Understanding Your Health History
Your doctor needs a complete health history. This includes details about your current health, any past medical conditions (like heart problems or bleeding disorders), and medications you’re taking. They’ll ask about allergies and your pregnancy details (if applicable), including the estimated gestational age. Accurate information ensures safe and effective treatment.
Assessing Your Situation
- Discuss your options. Your doctor can provide information on various methods for managing an unwanted pregnancy, including medical and surgical abortion.
- Confirm pregnancy. A blood or urine test will verify pregnancy before any medication is considered.
- Determine gestational age. This influences treatment plans and the likely success rate of medication abortion.
- Rule out ectopic pregnancy. This serious condition requires immediate medical attention and cannot be treated with misoprostol.
Managing Potential Risks
Misoprostol, like any medication, carries potential side effects. These can range from mild (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) to more serious (heavy bleeding, infection). Your doctor will discuss these risks and explain how to manage them.
Post-Treatment Follow-Up
- Schedule a follow-up appointment. This allows your doctor to monitor your progress and address any complications.
- Discuss contraception. Your doctor will help you choose the most suitable birth control method after your treatment.
- Know when to seek immediate care. Understand the signs of serious complications and when to contact your doctor or go to the emergency room.
Finding Reliable Information
Use reputable sources for medical information. Consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider rather than relying on unreliable websites or social media.
Alternative Treatment Options
Discuss all available options with your doctor. Depending on your circumstances, other treatments may be more suitable or preferable.
Finding Reliable Information on Misoprostol
Prioritize information from reputable sources. The World Health Organization (WHO) website offers evidence-based guidelines on medication abortion. Similarly, several major medical organizations, like the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), provide detailed, medically accurate information.
Checking Source Credibility
- Look for websites with “.gov” (government) or “.org” (non-profit organization) domain extensions, indicating a higher likelihood of unbiased, factual information.
- Check the “About Us” section to verify the source’s expertise and credentials. Doctors, medical professionals, and established health organizations are better sources than blogs or personal anecdotes.
- Evaluate the date of publication. Medical information evolves; recent publications are preferred. Older information might be outdated or inaccurate.
- Verify information by consulting multiple reliable sources. If multiple reputable sources concur, you have a stronger basis for confidence.
Accessing Reliable Information
- Consult your doctor or other healthcare provider. They can answer specific questions about Misoprostol and its usage, considering your individual health situation.
- Seek out telemedicine platforms offering reputable, licensed medical consultations. These services often provide accurate information and guidance.
- Use search engines carefully. Filter search results by specifying “medical websites” or “health organizations” to narrow down your search to trustworthy sources.
Avoiding Misinformation
Be wary of information from unverified websites, social media posts, or forums. Misinformation abounds online, leading to potentially dangerous consequences. Always check the source’s reliability before acting on the information you find.
Understanding Limitations
Remember that online information shouldn’t replace professional medical advice. While research is valuable, a doctor’s consultation is vital for safe and effective use of Misoprostol.
Emergency Contraception vs. Misoprostol for Abortion
Emergency contraception, like the morning-after pill, prevents pregnancy after unprotected sex. It’s different from misoprostol, which induces abortion by ending an existing pregnancy. Emergency contraception works best within 72 hours of unprotected sex, while misoprostol’s effectiveness decreases as the pregnancy progresses.
Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraception contains high doses of hormones that delay or prevent ovulation. It does not affect an already implanted embryo. Several types exist, including levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate. These are available over-the-counter at pharmacies. Consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns or questions about its use.
Misoprostol for Abortion
Misoprostol, when used for abortion, causes uterine contractions that expel the pregnancy. It’s most effective within the first 10 weeks of pregnancy. While sometimes available over the counter in some countries, its usage for abortion requires careful medical guidance. Self-administering misoprostol without professional supervision can be dangerous and lead to complications. Always seek medical advice before using misoprostol to induce an abortion.
Key Differences
Purpose: Emergency contraception prevents pregnancy; misoprostol terminates an existing pregnancy. Timing: Emergency contraception is most effective shortly after unprotected sex; misoprostol’s effectiveness depends on gestational age. Mechanism: Emergency contraception prevents ovulation; misoprostol induces uterine contractions. Safety: Both have potential side effects, but misoprostol carries greater risks if used incorrectly or outside the recommended timeframe. Always consult a medical professional for safe and appropriate use of either method.