Gabapentin primarily treats nerve pain (neuropathic pain) and epilepsy. Doctors also prescribe it for restless legs syndrome and fibromyalgia.
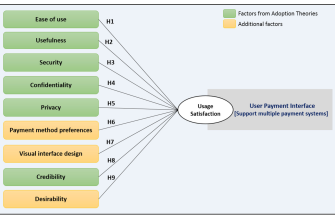
Dosage and Administration
Your doctor determines the correct dosage based on your condition and response to treatment. Typical starting doses range from 300 to 900 mg daily, often divided into multiple doses. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Common Side Effects
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Headache
These side effects are usually mild and temporary. If you experience severe or persistent side effects, contact your doctor immediately. Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to minimize potential drug interactions.
Serious Side Effects (Seek Immediate Medical Attention)
- Severe allergic reactions (difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue)
- Suicidal thoughts or behaviors
- Unusual bruising or bleeding
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your individual health status and medical history.
Potential Interactions
Gabapentin can interact with various medications, including opioids, benzodiazepines, and other central nervous system depressants. Combining Gabapentin with alcohol can significantly increase the risk of drowsiness and other side effects. Open communication with your doctor about all medications and substances you consume is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
Specific Considerations
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor before taking gabapentin if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding.
- Older adults: Older adults may be more susceptible to side effects. Your doctor may adjust the dosage accordingly.
- Kidney problems: Gabapentin is excreted through the kidneys; individuals with kidney problems require careful dose adjustments.
Long-Term Use
Long-term use of gabapentin may require regular monitoring by your doctor to assess its effectiveness and identify any potential long-term side effects. Regular check-ups are paramount for ensuring safe and effective management of your condition.
Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
Gabapentin’s effects can be altered by other medications and substances. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs. This includes opioid pain relievers, benzodiazepines, and antidepressants. Combining gabapentin with these can increase drowsiness and impair coordination, potentially leading to falls or accidents. Avoid alcohol completely while taking gabapentin; the combination significantly magnifies sedation and increases the risk of respiratory depression.
Opioids and Sedatives
Concomitant use of gabapentin with opioids, such as morphine or oxycodone, or sedatives like benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam, alprazolam), significantly enhances the central nervous system depressant effects. This interaction can result in increased drowsiness, dizziness, respiratory depression, and even coma. Monitor yourself closely for these symptoms and contact your doctor immediately if you experience them.
Antacids
Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium may reduce gabapentin absorption. Separate the administration of gabapentin and antacids by at least two hours to minimize this interaction. Your doctor can provide further guidance regarding optimal timing.
Other Medications
Gabapentin may interact with certain anticonvulsants, altering their effectiveness. Similarly, some medications metabolized by the liver might have altered clearance when taken with gabapentin. This requires careful monitoring by your physician. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for a complete list of potential interactions specific to your situation. They can adjust dosages or suggest alternatives if necessary.