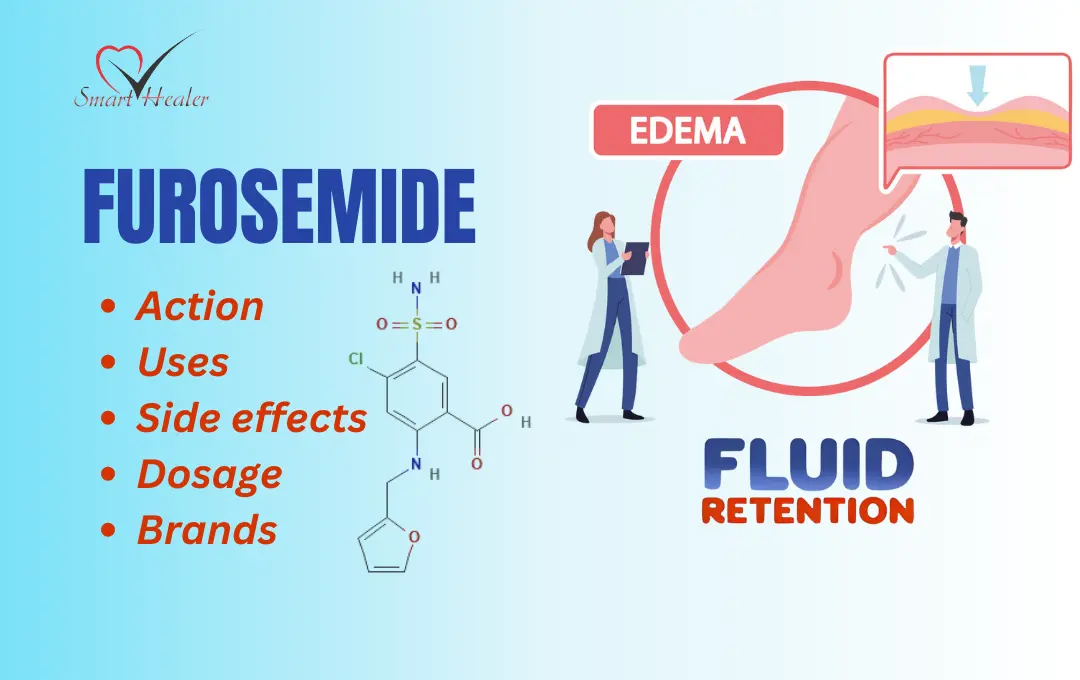
Experiencing side effects from Furosemide? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. Many people taking this medication report some degree of side effects, ranging from mild to more serious. Understanding these potential reactions is key to managing your treatment effectively.
Common side effects include dizziness, dehydration, and frequent urination. These often lessen as your body adjusts, but staying hydrated is crucial to mitigating these symptoms. Drink plenty of water and consider electrolyte drinks if needed. Always consult your doctor if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms.
Less common, but still possible, side effects involve changes in hearing, muscle cramps, and low blood pressure. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience sudden hearing loss, severe muscle pain, or faintness. These are indications of potentially serious problems needing prompt medical intervention.
Before starting Furosemide, provide your doctor with a complete medical history, including any existing conditions, particularly heart or kidney problems. This proactive approach helps minimize potential risks and personalize your treatment plan. Regular check-ups are recommended to monitor your progress and adjust your medication as needed.
- Furosemide Side Effects: A Detailed Guide
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common but Serious Side Effects
- Managing Side Effects
- Common Side Effects of Furosemide
- Serious Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- Long-Term Side Effects and Management
- Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
- Lithium
- Digoxin
- Aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin, tobramycin)
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Alcohol
- Potassium-depleting medications
- Metformin
- Antacids
- Warfarin
- Other Considerations
- When to Contact Your Doctor Regarding Furosemide Side Effects
- Less Severe, But Still Important Side Effects
- When to Report Changes
- Don’t Hesitate
Furosemide Side Effects: A Detailed Guide
Consult your doctor immediately if you experience severe dizziness or lightheadedness. These can be signs of dehydration, a common furosemide side effect. Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial; drink plenty of water unless specifically advised otherwise by your physician.
Common Side Effects
Expect potential mild side effects like increased urination, thirst, and muscle cramps. These are usually manageable by adjusting fluid intake and potentially adding potassium supplements, as prescribed by your doctor. Dietary changes, such as increasing potassium-rich foods like bananas and spinach, might also help. Regular blood tests will monitor your electrolyte balance.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
While less frequent, you should be aware of potential side effects like hearing loss, which might be temporary or persistent, and low blood pressure (hypotension), potentially causing fainting. Report any changes in hearing immediately to your healthcare provider. Hypotension can be managed through careful monitoring and medication adjustments. You should also monitor your blood sugar levels as furosemide can affect blood glucose levels.
Managing Side Effects
Your doctor will create a personalized management plan. This might involve adjustments to your furosemide dosage, dietary modifications, or additional medications to address specific side effects. Open communication with your healthcare team is key to successful treatment and side effect management. Regular check-ups allow for prompt adjustments as needed.
Common Side Effects of Furosemide
Furosemide, a powerful diuretic, commonly causes dehydration. Drink plenty of fluids to mitigate this.
Low blood pressure (hypotension) is another frequent side effect. You might experience dizziness or lightheadedness. Rise slowly from a sitting or lying position to avoid falls.
Electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium (hypokalemia), are possible. Your doctor may recommend a potassium supplement or dietary changes.
Muscle cramps and weakness are often associated with potassium depletion. Increased potassium intake through diet may help.
Increased thirst and urination are expected effects of furosemide’s diuretic action. Adjust fluid intake as needed to manage this.
Hearing loss is a less common but potential side effect, usually temporary. Report any hearing changes to your doctor immediately.
Drowsiness or fatigue can occur. Avoid driving or operating machinery if affected.
Allergic reactions, such as rash or itching, are possible. Stop taking furosemide and seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms.
Consult your doctor if you experience any concerning side effects. They can help manage these and adjust your treatment as needed.
Serious Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical help if you experience any of the following: Severe allergic reactions, including hives, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, or a fast heartbeat. These are life-threatening and need urgent attention.
Dehydration is another serious concern. Watch for extreme thirst, decreased urination, dizziness, or lightheadedness. These symptoms indicate a significant fluid loss and require prompt medical evaluation.
Hearing loss or ringing in your ears (tinnitus) can be signs of ototoxicity, a potentially irreversible side effect. Report these symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Sudden weakness or muscle cramps could signify electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium (hypokalemia). These imbalances can disrupt heart rhythm and require careful monitoring and treatment.
Changes in your vision, including blurred vision or jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), should be reported to your doctor without delay. These could indicate serious liver problems.
If you experience unusual fatigue, confusion, or irregular heartbeat, consult a doctor immediately. These symptoms could indicate more serious underlying issues.
Remember: This list is not exhaustive. Any new or worsening symptoms while taking furosemide should be reported to your healthcare provider. Your doctor can assess your individual risk and provide the appropriate care.
Long-Term Side Effects and Management
Regularly monitor potassium levels. Low potassium (hypokalemia) is a common long-term risk. Your doctor will likely recommend blood tests to track this.
Maintain adequate hydration. Furosemide’s diuretic effect can lead to dehydration. Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, unless your doctor advises otherwise.
Watch for hearing changes. Tinnitus or hearing loss, though rare, can occur with prolonged use. Report any such changes immediately to your physician.
- Report any dizziness or lightheadedness. These symptoms may indicate low blood pressure.
- Adjust your diet. Consider increasing your intake of potassium-rich foods like bananas, potatoes, and spinach to counteract potential hypokalemia.
Consult your doctor about alternative medications. If long-term side effects become problematic, explore other diuretics or treatment strategies with your doctor.
- Regularly review your medication list with your doctor. This helps identify potential drug interactions and adjust dosages as needed.
- Be aware of potential interactions with other medications. Some medications can exacerbate furosemide’s side effects or reduce its effectiveness. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the medications you are taking.
Consider lifestyle changes. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can improve overall health and potentially mitigate some of the side effects.
Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting furosemide. This includes over-the-counter drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen.
Lithium
Furosemide can increase lithium levels in your blood, potentially leading to lithium toxicity. Your doctor will need to monitor your lithium levels closely if you’re taking both medications.
Digoxin
Combining furosemide with digoxin might lower potassium levels, increasing the risk of digoxin toxicity. Regular potassium level checks are necessary.
Aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin, tobramycin)
Furosemide enhances the risk of aminoglycoside-induced hearing loss by promoting fluid loss. Your doctor should carefully assess the potential risks and benefits.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs can reduce furosemide’s effectiveness. This interaction can decrease furosemide’s ability to lower blood pressure and eliminate fluid. Your doctor may adjust your dosage accordingly.
Alcohol
Alcohol consumption while on furosemide increases the risk of dehydration and low blood pressure. Limit alcohol intake significantly.
Potassium-depleting medications
Concurrent use with other drugs that lower potassium (such as corticosteroids or laxatives) increases the risk of dangerously low potassium levels (hypokalemia). Regular blood tests are crucial.
Metformin
The combination of furosemide and metformin might raise the risk of lactic acidosis, a serious condition. Your doctor will closely monitor you for signs.
Antacids
Some antacids can affect furosemide absorption. Consult your doctor or pharmacist about appropriate timing of medication intake.
Warfarin
Furosemide can impact how your body processes warfarin, potentially altering bleeding risks. Your doctor will monitor your blood clotting time regularly.
Other Considerations
Note: This is not an exhaustive list. Many other drug interactions are possible. Always consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist before combining furosemide with any other substance. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific medical condition and other medications you are taking.
When to Contact Your Doctor Regarding Furosemide Side Effects
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any severe side effects. This includes symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling in your face, lips, or tongue (angioedema), irregular heartbeat, or severe dizziness.
Less Severe, But Still Important Side Effects
While less alarming, certain side effects warrant a call to your doctor. These include persistent nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle cramps, or unusual fatigue. Regular monitoring is crucial for managing these side effects and ensuring your treatment remains safe and effective.
When to Report Changes
Report any significant changes in your health, even if seemingly unrelated to furosemide. This includes sudden weight changes, unusual thirst, or changes in your urine output. These could indicate issues needing immediate attention.
| Side Effect | When to Contact Doctor |
|---|---|
| Difficulty breathing, facial swelling | Immediately |
| Irregular heartbeat, severe dizziness | Immediately |
| Persistent nausea/vomiting/diarrhea | Within 24 hours |
| Muscle cramps, unusual fatigue | Within 24-48 hours |
| Significant weight change, altered thirst/urination | As soon as possible |
Don’t Hesitate
Open communication with your doctor is key to successful treatment. Don’t hesitate to contact them with any concerns, regardless of severity. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes.