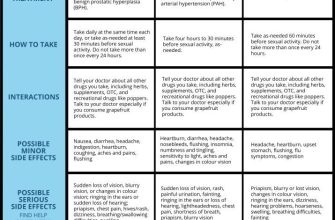
Need to understand Dinoprostone? Focus on its role in cervical ripening and labor induction. This medication isn’t a universal solution, so understanding its proper application is key. We’ll cover its administration methods, potential side effects, and crucial safety precautions.
Administering Dinoprostone requires precise techniques. Intracervical insertion is common, involving careful placement to maximize efficacy and minimize discomfort. Dosage strictly follows medical guidelines; variations necessitate close monitoring and physician consultation. Never deviate from prescribed protocols.
Potential side effects include uterine hyperstimulation, fetal heart rate changes, and postpartum hemorrhage. Close monitoring of both mother and fetus is mandatory throughout the process. Recognizing these potential complications allows for prompt intervention, ensuring maternal and fetal well-being.
Remember: Dinoprostone is a powerful medication. Its use should always be under the direct supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. This guide provides information; it does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before using Dinoprostone or any other medication.
- Administration Routes and Dosage Regimens
- Vaginal Route
- Intravenous Route
- Important Considerations
- Dosage Adjustments and Contraindications
- Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Medications Affecting Uterine Contractility
- Other Potential Interactions
- Reporting Adverse Effects
Administration Routes and Dosage Regimens
Dinoprostone is administered via several routes, each with specific dosage recommendations. Cervical ripening typically uses vaginal inserts or a gel. For labor induction, intravenous administration is common.
Vaginal Route
Vaginal inserts: These are typically 20 mg. The number of inserts and frequency depend on the individual patient’s response and clinical situation. Your healthcare provider will carefully monitor progress and adjust the regimen accordingly.
Vaginal gel: Dosage ranges from 0.5 mg to 2 mg, applied at intervals determined by your doctor based on your progress.
Intravenous Route
Intravenous infusion: Intravenous administration is used specifically for labor induction. The initial dose is commonly followed by a continuous infusion at a rate adjusted based on the patient’s response and medical needs. Exact dosage parameters are highly individualized and determined by the attending physician.
Important Considerations
Dosage adjustments are frequently necessary based on individual patient responses and medical history. Close monitoring of vital signs and fetal heart rate is crucial. Always follow your healthcare provider’s specific instructions.
Dosage Adjustments and Contraindications
Dosage reduction or discontinuation might be necessary in response to adverse effects such as uterine hyperstimulation or fetal distress. Pre-existing conditions such as asthma, cardiovascular disease, or glaucoma can influence the dosage and administration method. Always consult a physician about pre-existing conditions before using dinoprostone.
Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Dinoprostone, while effective, can cause various side effects. Fever and chills are common, often resolving without intervention. You may experience nausea and vomiting; antiemetics can help manage these symptoms.
Uterine hyperstimulation is a serious concern. This manifests as excessively strong or frequent contractions. Close monitoring is crucial to detect and manage this complication. Pain is another expected side effect; your healthcare provider will discuss pain management strategies.
Hypotension (low blood pressure) and tachycardia (rapid heart rate) are potential cardiovascular effects. These are usually mild and transient. However, pre-existing cardiovascular conditions necessitate careful monitoring.
Allergic reactions, though rare, can occur. Symptoms may include rash, itching, or swelling. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience an allergic reaction.
Postpartum hemorrhage is a possible complication, requiring prompt medical intervention. Your doctor will discuss strategies to minimize this risk.
This information is not exhaustive; consult your physician for a complete discussion of potential risks and benefits.
Interactions with Other Medications
Dinoprostone’s effects can be altered by other medications. Always inform your doctor of all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal remedies, and supplements. This includes prescription drugs, vitamins, and even some foods.
Medications Affecting Uterine Contractility
Certain medications can either enhance or reduce Dinoprostone’s effect on uterine contractions. For example, oxytocin, another medication used to induce labor, will likely increase uterine stimulation when used in conjunction with Dinoprostone. Conversely, medications that relax the uterus, such as magnesium sulfate, may counteract Dinoprostone’s action. Your doctor will carefully assess your situation to determine the appropriate approach.
Other Potential Interactions
While less common, Dinoprostone may interact with medications that affect blood clotting. This means anticoagulants or blood thinners need to be carefully managed during Dinoprostone administration to reduce the risk of excessive bleeding. Similarly, it’s crucial to discuss any use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with your physician before using Dinoprostone, as these can affect the medication’s efficacy.
Remember: This information is not exhaustive and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking any medication, especially during pregnancy or childbirth.
Reporting Adverse Effects
Report any unusual symptoms experienced while taking Dinoprostone to your healthcare provider immediately. This allows them to adjust your treatment plan and ensure your safety.