Consult your doctor before using Azithromycin; it’s crucial for personalized treatment plans.
Understanding Azithromycin
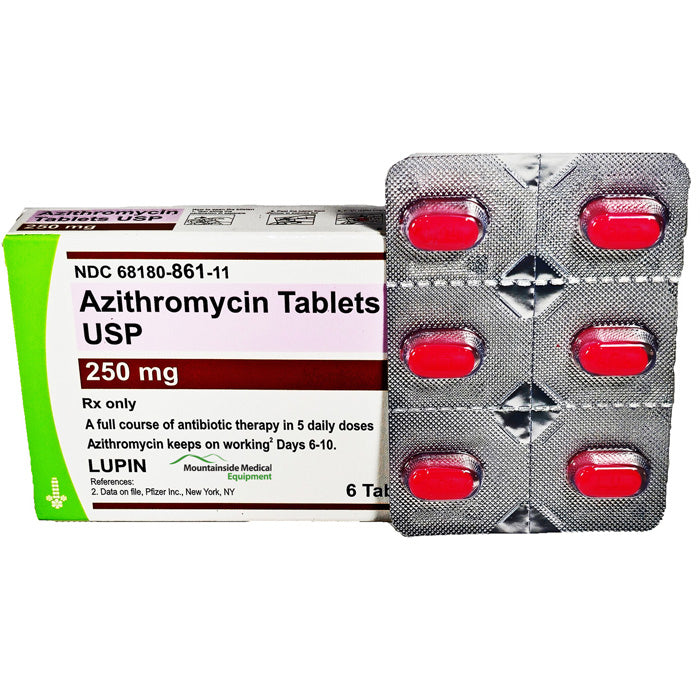
Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic, effective against a range of bacterial infections. It works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, preventing their growth and reproduction. Common uses include treating respiratory infections like bronchitis and pneumonia, certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia, and skin infections.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage varies significantly based on the infection, your age, and overall health. Your physician will determine the appropriate dose and duration. Typically, Azithromycin is taken orally, as tablets or suspension.
- Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor.
- Follow the prescribed regimen meticulously. Incomplete courses can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Potential Side Effects
While generally safe, Azithromycin can cause side effects. These can include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. More serious, though rare, side effects include allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling), heart problems, and liver damage. Report any unusual symptoms immediately to your healthcare provider.
Drug Interactions
Azithromycin interacts with several medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking before starting Azithromycin. This interaction check is essential to prevent potentially harmful consequences.
Contraindications
People with known allergies to Azithromycin or other macrolide antibiotics should avoid this medication. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should discuss use with their doctor. Kidney or liver impairment can also affect dosage and safety.
Seeking Medical Advice
This information isn’t a substitute for professional medical advice. Always discuss Azithromycin use with your doctor before taking it. They can assess your individual needs and determine the optimal course of treatment.
Beyond the Basics
Long-Term Effects and Resistance
Prolonged use of Azithromycin can contribute to antibiotic resistance. Your doctor will consider this carefully when prescribing it. Responsible antibiotic use is vital for public health.
Alternative Treatments
Depending on your specific infection, alternative treatments may be available. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and risks of different options to create the most effective treatment plan for your individual situation.
Dosage and Administration: Understanding the Prescription
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Azithromycin dosage varies significantly depending on the infection being treated, your age, and your overall health. Typical adult dosages range from 500mg as a single dose to 500mg daily for 3-5 days, or other regimens as prescribed. Children’s dosages are significantly lower and calculated based on weight.
Azithromycin comes in various forms: tablets, capsules, oral suspension (liquid), and intravenous formulations. Your doctor will specify the most appropriate form for your condition. Take oral forms with a full glass of water, usually on an empty stomach (at least one hour before or two hours after a meal) for better absorption. Don’t crush or chew extended-release tablets.
If using the oral suspension, carefully measure the dose using the measuring device provided. Always shake the suspension well before each use to ensure even distribution of the medication. For intravenous administration, a healthcare professional will administer the medication.
Complete the entire course of treatment, even if you start feeling better before finishing all your medication. Stopping early can lead to treatment failure and potential recurrence of the infection. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses.
Report any side effects to your doctor immediately. Common side effects may include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Serious side effects are less common but require prompt medical attention.
Proper storage is crucial. Store Azithromycin tablets and capsules at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Oral suspensions should be refrigerated and discarded after the expiration date on the label.
This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for specific dosage instructions and to discuss any concerns you may have.